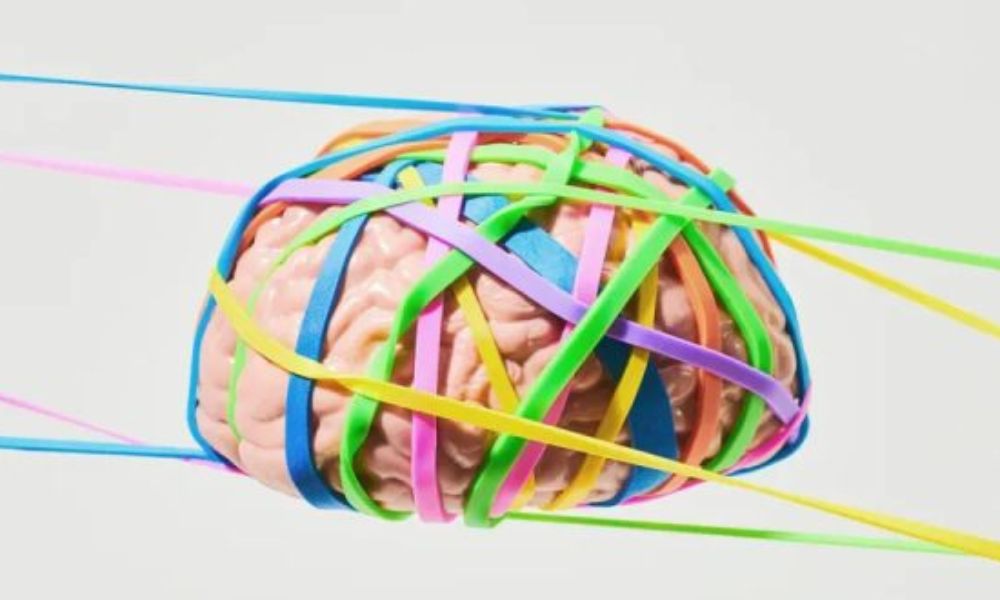
The human brain is constantly reshaping and rewiring itself in response to experiences and challenges. This remarkable ability, known as neuroplasticity, is often likened to the elasticity of a rubber band – the brain can stretch and flex to accommodate new information, skills, and circumstances.
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s capacity to form and reorganize synaptic connections, allowing for learning, memory formation, and recovery from injury. It enables us to acquire new skills, adapt to changes in our environment, and recover from brain damage. Understanding the principles of neuroplasticity can empower us to actively engage in activities that promote brain health and cognitive function throughout our lives.
The Incredible Elastic Brain
Imagine your brain as a dynamic network of billions of neurons, constantly communicating and forming connections. Neuroplasticity is the mechanism through which this network adapts and evolves in response to stimuli. When we learn something new, whether it’s a language, a musical instrument, or a new hobby, our brain physically changes as neural connections are strengthened and new pathways are formed.
Keeping Your Brain Elastic
Just like exercising a muscle to keep it strong and flexible, there are various ways to promote neuroplasticity and maintain the elasticity of your brain:
- Play Brain Games: Engaging in activities that challenge your cognitive abilities, such as puzzles, memory games, and strategic board games, can stimulate neuroplasticity. These activities encourage the formation of new neural connections and help maintain cognitive function.
- Stay Physically Active: Regular exercise has been shown to enhance neuroplasticity by increasing blood flow to the brain and promoting the release of growth factors that support the growth of new neurons and synaptic connections.
- Learn New Skills: Whether it’s learning a musical instrument, mastering a new language, or taking up a new hobby, engaging in lifelong learning activities can stimulate neuroplasticity and keep your brain sharp.
- Socialize: Interacting with others and maintaining social connections can also support brain health and cognitive function. Meaningful social engagement has been linked to improved cognitive performance.
Factors That Decrease Neuroplasticity
While the brain is incredibly adaptable, certain factors can hinder neuroplasticity and impair cognitive function:
- Stress: Chronic stress can have detrimental effects on the brain, inhibiting neuroplasticity and impairing memory and learning.
- Aging: As we age, changes occur in the structure and function of the brain, including a reduction in neuroplasticity. However, engaging in activities that promote brain health can help mitigate age-related decline.
- Sleep Deprivation: Lack of sleep can disrupt neural processes involved in memory consolidation and learning, impairing cognitive function and reducing neuroplasticity.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Physical inactivity can negatively impact brain health and cognitive function, reducing neuroplasticity and increasing the risk of cognitive decline.
Conclusion
The elasticity of the human brain is a testament to its remarkable capacity for adaptation and growth. By understanding the principles of neuroplasticity and actively engaging in activities that promote brain health and enjoy a higher quality of life throughout our lifespan. So, challenge your mind, stay active, and nurture your brain – it’s the most incredible organ you’ll ever own.













More Stories
Why Do People Act Strangely After an Accident?
‘Workplace Stress’ – A new Pandemic! Impacts health, taking lives…
Understand Anxiety